- When An Atom Gains An Electron It Becomes A Positive Ion True Or False
- When An Atom Gains An Electron It Becomes A Cation
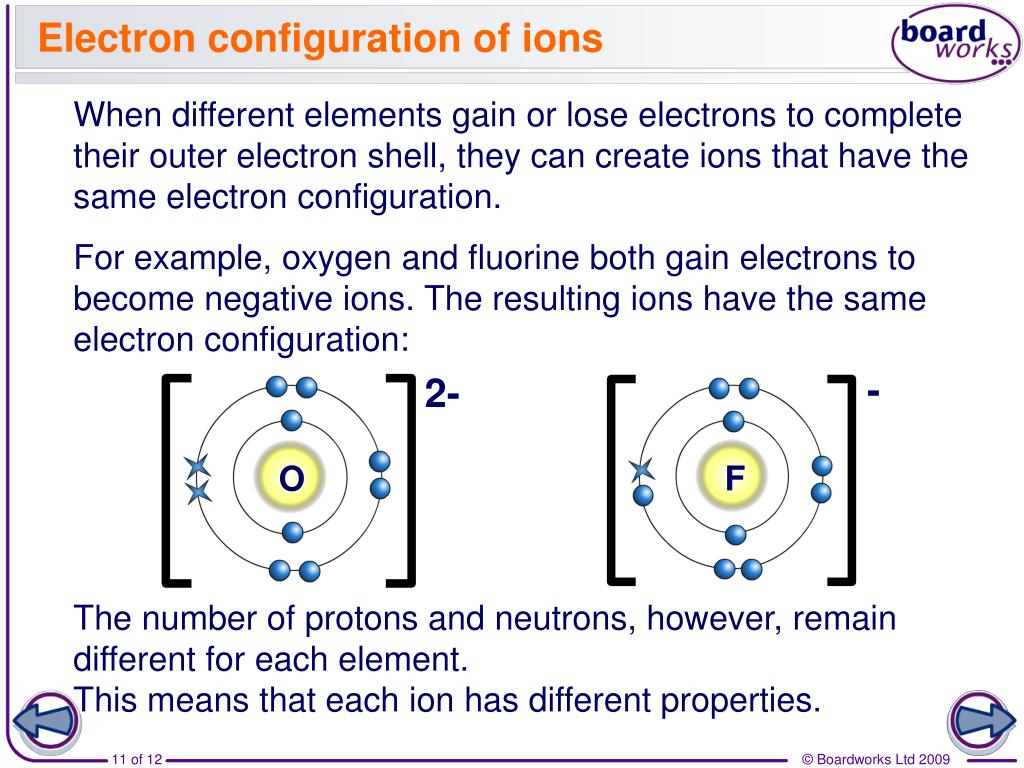
Most atoms do not have eight electrons in their valence electron shell. Some atoms have only a few electrons in their outer shell, while some atoms lack only one or two electrons to have an octet. In cases where an atom has three or fewer valence electrons, the atom may lose those valence electrons quite easily until what remains is a lower shell that contains an octet. Atoms that lose electrons acquire a positive charge as a result because they are left with fewer negatively charged electrons to balance the positive charges of the protons in the nucleus. Positively charged ions are called cations. Most metals become cations when they make ionic compounds.
Select all the true statements. When an atom gains an electron, it becomes a cation. Anions carry a positive charge. The cl− and br− ions have the same number of electrons. The k+ ion is formed when a potassium atom loses one electron. The fe2+ and fe3+ ions have the same number of protons. The cu+ and cu2+ ions have the same number of electrons. When atoms gain electrons, they become negatively charged. Atoms losing electrons become positively charged. In a neutral atom, the number of electrons orbiting the nucleus equals the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom. Protons are the positive particles in an atom, while electrons are the negative ones. Select all the true statements. When an atom gains an electron, it becomes a cation. The Cl- and Brions have the same number of electrons. The Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions have the same number of protons. The Cut and Cu2+ ions have the same number of electrons. The K+ ion is formed when a potassium atom loses one electron. Anions carry a positive charge. Here is the answer for the question – If an atom gains or loses electrons it becomes. You’ll find the correct answer below If an atom gains or loses electrons it becomes The Correct Answer is an ion.Explanation: An ion is a charged atom or molecule that has gained or lost electrons Reason Explained an.
Cations
A neutral sodium atom is likely to achieve an octet in its outermost shell by losing its one valence electron.
[ce{Na rightarrow Na^{+} + e^{-}}]
The cation produced in this way, Na+, is called the sodium ion to distinguish it from the element. The outermost shell of the sodium ion is the second electron shell, which has eight electrons in it. The octet rule has been satisfied. Figure (PageIndex{1}) is a graphical depiction of this process.
 and a negatively charged ion (anion).jpg)
Anions
Some atoms have nearly eight electrons in their valence shell and can gain additional valence electrons until they have an octet. When these atoms gain electrons, they acquire a negative charge because they now possess more electrons than protons. Negatively charged ions are called anions. Most nonmetals become anions when they make ionic compounds.
A neutral chlorine atom has seven electrons in its outermost shell. Only one more electron is needed to achieve an octet in chlorine’s valence shell. (In table salt, this electron comes from the sodium atom.)
[ce{e^{-} +Cl -> Cl^{-}}]
In this case, the ion has the same outermost shell as the original atom, but now that shell has eight electrons in it. Once again, the octet rule has been satisfied. The resulting anion, Cl−, is called the chloride ion; note the slight change in the suffix (-ide instead of -ine) to create the name of this anion. Figure (PageIndex{2}) is a graphical depiction of this process.
The names for positive and negative ions are pronounced CAT-eye-ons and ANN-eye-ons, respectively.
In many cases, elements that belong to the same group (vertical column) on the periodic table form ions with the same charge because they have the same number of valence electrons. Thus, the periodic table becomes a tool for remembering the charges on many ions. For example, all ions made from alkali metals, the first column on the periodic table, have a 1+ charge. Ions made from alkaline earth metals, the second group on the periodic table, have a 2+ charge. On the other side of the periodic table, the next-to-last column, the halogens, form ions having a 1− charge. Figure (PageIndex{3}) shows how the charge on many ions can be predicted by the location of an element on the periodic table. Note the convention of first writing the number and then the sign on a multiply charged ion. The barium cation is written Ba2+, not Ba+2.

Contributors and Attributions
Marisa Alviar-Agnew (Sacramento City College)
Henry Agnew (UC Davis)
Learning Objective
- Summarize the characteristic features of ionic bonds

Key Points
- Ionic bonds are formed through the exchange of valence electrons between atoms, typically a metal and a nonmetal.
- The loss or gain of valence electrons allows ions to obey the octet rule and become more stable.
- Ionic compounds are typically neutral. Therefore, ions combine in ways that neutralize their charges.
Terms
- valence electronsThe electrons of an atom that can participate in the formation of chemical bonds with other atoms. They are the furthest electrons from the nucleus.
- octet ruleAn atom is most stable when there are eight electrons in its valence shell.
Forming an Ion
Ionic bonds are a class of chemical bonds that result from the exchange of one or more valence electrons from one atom, typically a metal, to another, typically a nonmetal. Acrobat reader pro for mac. This electron exchange results in an electrostatic attraction between the two atoms called an ionic bond. An atom that loses one or more valence electrons to become a positively charged ion is known as a cation, while an atom that gains electrons and becomes negatively charged is known as an anion.
This exchange of valence electrons allows ions to achieve electron configurations that mimic those of the noble gases, satisfying the octet rule. The octet rule states that an atom is most stable when there are eight electrons in its valence shell. Atoms with less than eight electrons tend to satisfy the duet rule, having two electrons in their valence shell. By satisfying the duet rule or the octet rule, ions are more stable.
A cation is indicated by a positive superscript charge (+ something) to the right of the atom. An anion is indicated by a negative superscript charge (- something) to the right of the atom. For example, if a sodium atom loses one electron, it will have one more proton than electron, giving it an overall +1 charge. The chemical symbol for the sodium ion is Na+1 or just Na+. Similarly, if a chlorine atom gains an extra electron, it becomes the chloride ion, Cl–. Both ions form because the ion is more stable than the atom due to the octet rule.
Forming an Ionic Bond
Once the oppositely charged ions form, they are attracted by their positive and negative charges and form an ionic compound. Ionic bonds are also formed when there is a large electronegativity difference between two atoms. This difference causes an unequal sharing of electrons such that one atom completely loses one or more electrons and the other atom gains one or more electrons, such as in the creation of an ionic bond between a metal atom (sodium) and a nonmetal (fluorine).
Determining the Formula of an Ionic Compound
To determine the chemical formulas of ionic compounds, the following two conditions must be satisfied:
- Each ion must obey the octet rule for maximum stability.
- Ions will combine in a way that the overall ionic compound will be neutral. In other words, the charges of the ions must balance out.
Magnesium and fluorine combine to form an ionic compound. What is the formula for the compound?
Mg most commonly forms a 2+ ion. This is because Mg has two valence electrons and it would like to get rid of those two ions to obey the octet rule. Fluorine has seven valence electrons and usually forms the F – ion because it gains one electron to satisfy the octet rule. When Mg2+ and F – combine to form an ionic compound, their charges must cancel out. Therefore, one Mg2+ needs two F – ions to neutralize the charge. The 2+ of the Mg is balanced by having two -1 charged ions. Therefore, the formula of the compound is MgF2. The subscript two indicates that there are two fluorines that are ionically bonded to magnesium.
On the macroscopic scale, ionic compounds form crystalline lattice structures that are characterized by high melting and boiling points and good electrical conductivity when melted or solubilized.
Example
When An Atom Gains An Electron It Becomes A Positive Ion True Or False
Magnesium and fluorine combine to form an ionic compound. What is the formula for the compound?
Mg most commonly forms a 2+ ion. This is because Mg has two valence electrons and it would like to get rid of those two ions to obey the octet rule. Fluorine has seven valence electrons and as such, usually forms the F– ion because it gains one electron to satisfy the octet rule. When Mg2+ and F– combine to form an ionic compound, their charges must cancel out. Therefore, one Mg2+ needs two F– ions to balance. The 2+ of the Mg is balanced by having two -1 charged ions. Therefore, the formula of the compound is MgF2. The subscript two indicates that there are two fluorines that are ionically bonded to magnesium.
Show SourcesBoundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources:
http://www.boundless.com/
Boundless Learning
CC BY-SA 3.0.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/valence%20electrons
Wikipedia
CC BY-SA 3.0.

http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ionic_bond
Wikipedia
CC BY-SA 3.0.
When An Atom Gains An Electron It Becomes A Cation
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:NaF.gif
Wikipedia
CC BY-SA 3.0.
